Enquire Now
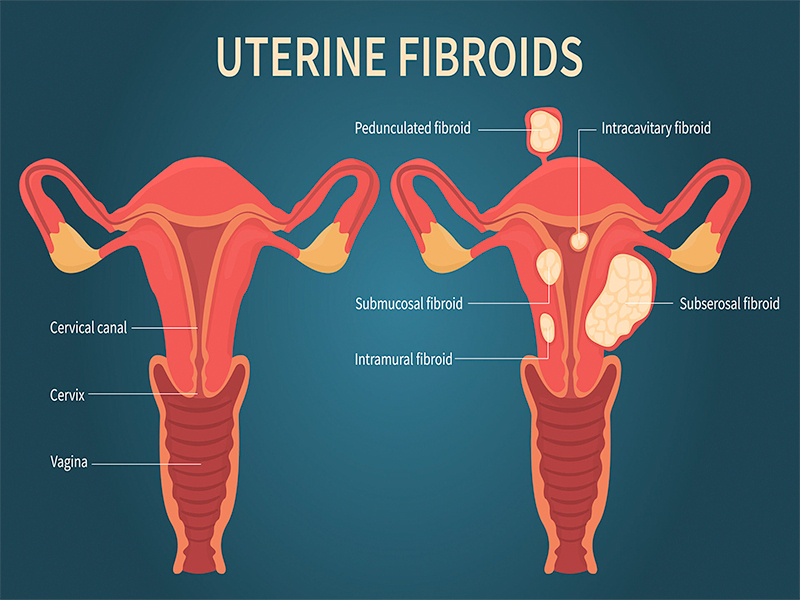
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. They are common, affecting up to 70% of women of reproductive age.
1. Intramural Fibroids : Grow within the muscular wall of the uterus.
2. Submucosal Fibroids : Grow into the uterine cavity, affecting menstrual flow and fertility.
3. Subserosal Fibroids : Grow on the outer surface of the uterus.
4. Pedunculated Fibroids : Grow on a stalk-like structure, attached to the uterus.
1. Heavy or Prolonged Menstrual Bleeding : Excessive bleeding, clots, or prolonged menstrual periods.
2. Pelvic Pain : Cramping, sharp pains, or dull aches in the lower abdomen.
3. Bloating and Discomfort : Feeling bloated, uncomfortable, or experiencing abdominal tenderness.
4. Infertility : Difficulty getting pregnant due to fibroids.
5. Frequent Urination : Pressure on the bladder from large fibroids.
1. Hormonal Imbalance : Estrogen dominance or hormonal fluctuations can contribute to fibroid growth.
2. Genetics : Family history of fibroids or other uterine conditions.
3. Age : Fibroids are more common in women of reproductive age.
4. Obesity : Excess weight can increase the risk of developing fibroids.
1. Pelvic Exam : A healthcare provider will perform a pelvic exam to check for tenderness, pain, or masses.
2. Imaging Tests : Ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be used to visualize the uterus and confirm the diagnosis.
3. Endometrial Biopsy : A biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions, such as endometrial cancer.
1. Watchful Waiting : Monitoring fibroid growth and symptoms.
2. Hormonal Therapies : Hormonal medications, such as birth control pills or progesterone, may be prescribed to reduce symptoms.
3. Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE) : A minimally invasive procedure that blocks blood flow to the fibroids.
4. Myomectomy : Surgical removal of fibroids, while leaving the uterus intact.
5. Hysterectomy : Surgical removal of the uterus, which may be recommended in severe cases.
Enquire Now